Cloud & Infrastructure
AWS Lambda Best Practices: A Comprehensive Guide
Learn the essential best practices for building efficient and scalable AWS Lambda functions, from memory management to error handling.
4/6/2024
8 min read
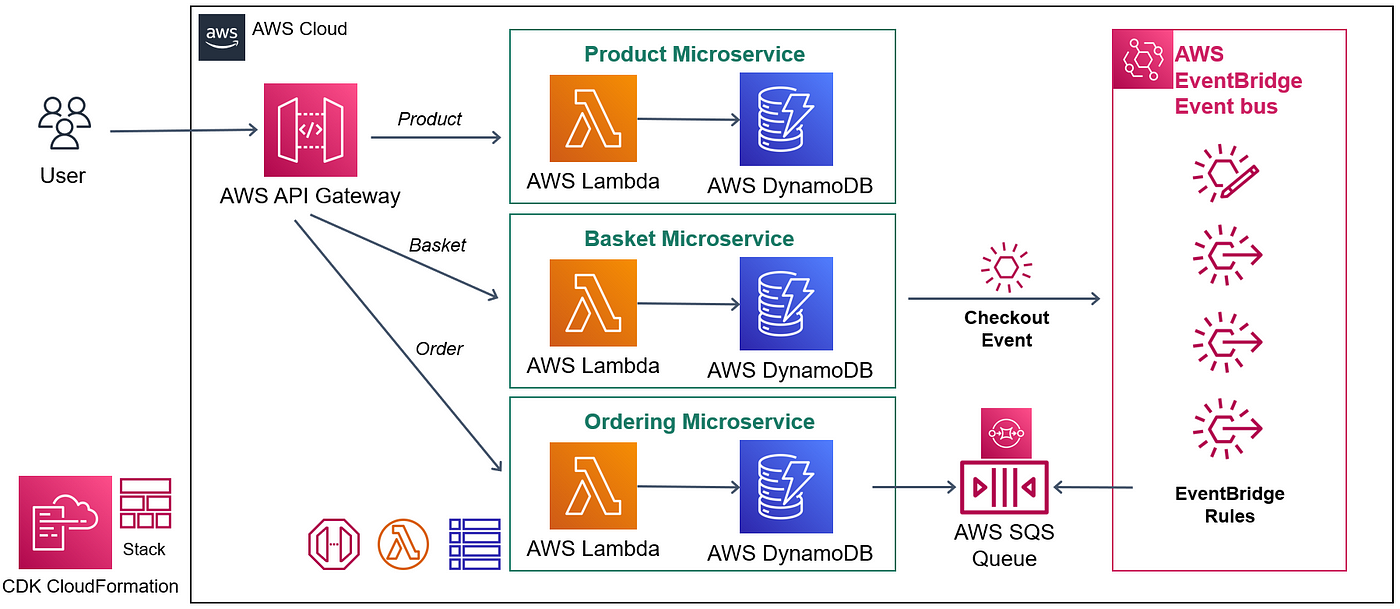
AWS Lambda Best Practices: A Comprehensive Guide
AWS Lambda has revolutionized serverless computing, but building efficient Lambda functions requires following certain best practices. In this guide, we’ll explore the key principles that will help you create robust and scalable Lambda functions.
1. Memory and Performance Optimization
Choose the Right Memory Size
- Start with 128MB and monitor performance
- Use CloudWatch metrics to identify optimal memory settings
- Consider the relationship between memory and CPU allocation
Optimize Package Size
- Remove unnecessary dependencies
- Use Lambda layers for common dependencies
- Keep deployment packages under 50MB unzipped
2. Error Handling and Logging
Implement Proper Error Handling
exports.handler = async (event) => {
try {
// Your function logic here
return {
statusCode: 200,
body: JSON.stringify({ message: "Success" }),
};
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error:", error);
return {
statusCode: 500,
body: JSON.stringify({ error: "Internal server error" }),
};
}
};Use Structured Logging
const log = {
timestamp: new Date().toISOString(),
level: "INFO",
message: "Processing request",
requestId: event.requestContext.requestId,
// Add relevant context
};
console.log(JSON.stringify(log));3. Cold Start Optimization
Keep Functions Warm
- Use provisioned concurrency for critical functions
- Implement keep-alive mechanisms
- Consider using Lambda Power Tuning tool
Optimize Dependencies
- Use lightweight runtimes
- Minimize initialization code
- Cache external service connections
4. Security Best Practices
Use IAM Roles Effectively
# Example IAM role with least privilege
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement":
[
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": ["dynamodb:GetItem", "dynamodb:PutItem"],
"Resource": "arn:aws:dynamodb:region:account:table/table-name",
},
],
}Implement Security Headers
const response = {
statusCode: 200,
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"X-Content-Type-Options": "nosniff",
"X-Frame-Options": "DENY",
"X-XSS-Protection": "1; mode=block",
},
body: JSON.stringify(data),
};5. Monitoring and Observability
Use CloudWatch Metrics
- Monitor invocation errors
- Track duration and memory usage
- Set up appropriate alarms
Implement Distributed Tracing
- Use AWS X-Ray for tracing
- Add correlation IDs
- Log request/response patterns
6. Cost Optimization
Optimize Function Duration
- Minimize external API calls
- Use connection pooling
- Implement caching where appropriate
Right-Size Resources
- Monitor actual usage patterns
- Adjust memory and timeout settings
- Use AWS Cost Explorer for analysis
Conclusion
Following these best practices will help you build more efficient, secure, and maintainable Lambda functions. Remember to:
- Monitor performance metrics
- Implement proper error handling
- Optimize cold starts
- Follow security best practices
- Use appropriate monitoring tools
- Optimize costs
Stay tuned for more AWS Lambda tips and tricks!
aws lambda serverless cloud best-practices